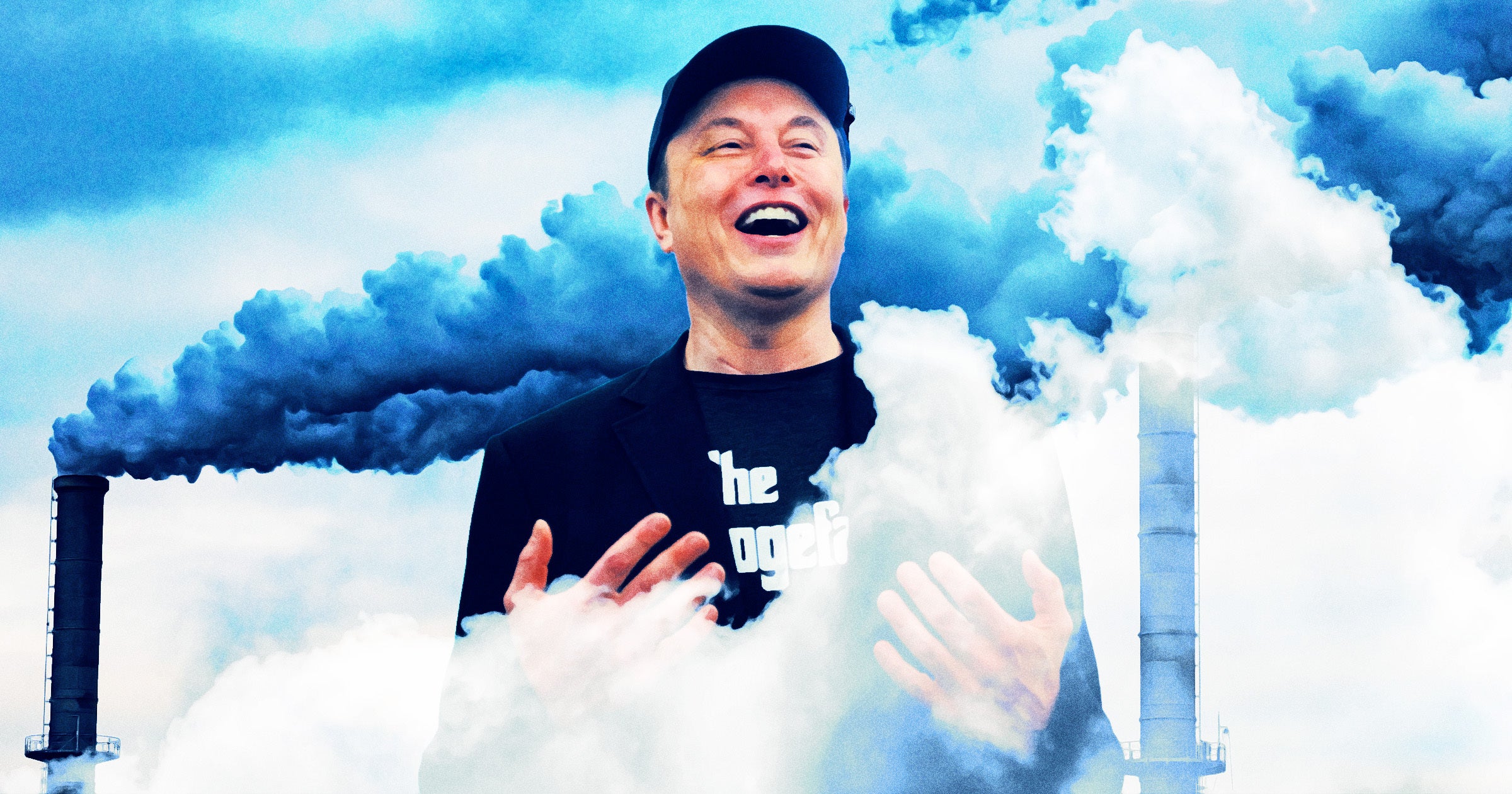
Regulatory authorities in Memphis, Tennessee, have granted a permit allowing Elon Musk’s startup xAI to continue emitting methane gas from its data center operations. The decision has sparked environmental concerns in a city historically recognized for its contributions to culture and music but now facing new industrial challenges.
xAI, an artificial intelligence company founded by Musk, operates a high-powered data center in Memphis—part of the company’s broader efforts to rival others in the AI industry. These facilities require vast amounts of energy to power and cool data-intensive servers around the clock. In this instance, the data center runs in part on methane-fueled generators, a choice that has drawn criticism due to the greenhouse gas’s potent effect on climate change and human health.
The permit approval allows the facility to continue its operations under specific emissions thresholds outlined by local environmental laws. Officials asserted that the emissions are within allowable limits and do not violate the Clean Air Act. However, environmental groups argue that the facility’s pollution contributes to worsened air quality and contradicts broader efforts to combat climate change.
Methane, while less abundant than carbon dioxide, is significantly more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere. Critics point out that approving such permits may set a concerning precedent as other tech companies build similar facilities across the U.S. Despite calls for increased oversight and cleaner operations, local authorities emphasized the economic benefits of the data center, including job creation and infrastructural investment.
As xAI continues to grow in the race to develop advanced AI technologies, debates around the environmental impact of its operations may intensify. The story underscores the emerging tension between innovation and sustainability, particularly as AI infrastructure becomes more energy-dependent.
Local stakeholders plan to monitor the center’s emissions closely, while environmental advocacy groups explore legal challenges and push for the inclusion of cleaner energy sources in future tech infrastructure planning.
Source: https:// – Courtesy of the original publisher.