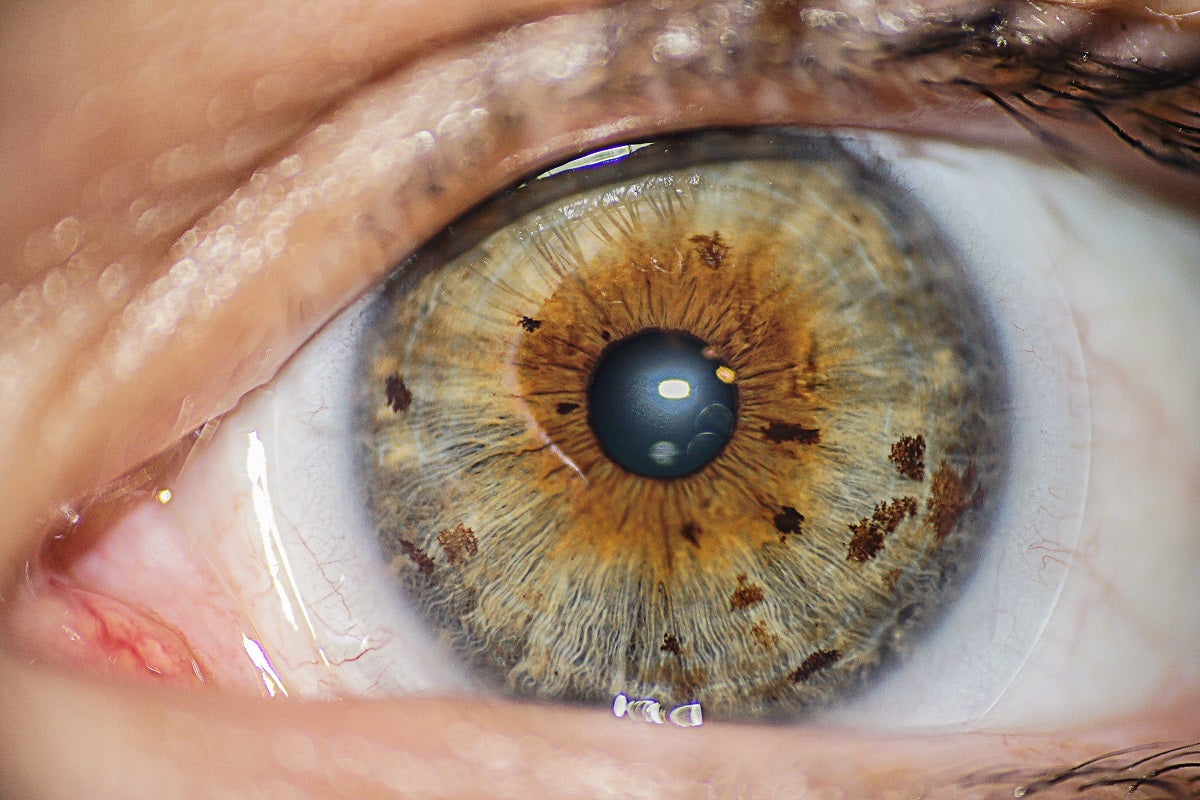
Scientists have found that gold particles could play a crucial role in restoring vision by replicating the functions of damaged photoreceptor cells in the eye. In new research, experts demonstrated that these nanoparticles can reproduce the electrical signals typically generated by healthy photoreceptors, which are essential for capturing and processing visual information.
Photoreceptors, located in the retina, are sensitive to light and are critical for vision. Damage to these cells, caused by conditions such as age-related macular degeneration or retinitis pigmentosa, often leads to significant vision loss or blindness. Current treatments are limited, but the new technique involving gold nanoparticles introduces a novel method of potentially reversing some of the effects of these degenerative diseases.
The study’s findings suggest that when injected into the eye, gold particles can effectively mimic the light-detecting and signal-transmitting functions of natural photoreceptors. This promising solution could pave the way for future therapies aimed at restoring vision to millions affected by retinal disorders.
Researchers are optimistic but caution that more extensive clinical testing is needed to determine the safety and effectiveness of the approach in humans. If successful, this breakthrough could represent a significant advancement in the field of ophthalmology and regenerative medicine.
Source: https:// – Courtesy of the original publisher.