Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly reshaping the landscape of grocery shopping with innovations that are changing how consumers interact with retailers and how stores operate behind the scenes. From personalized recommendations to fully automated stores and streamlined supply chains, these advancements are providing a new level of convenience and efficiency for both consumers and businesses.
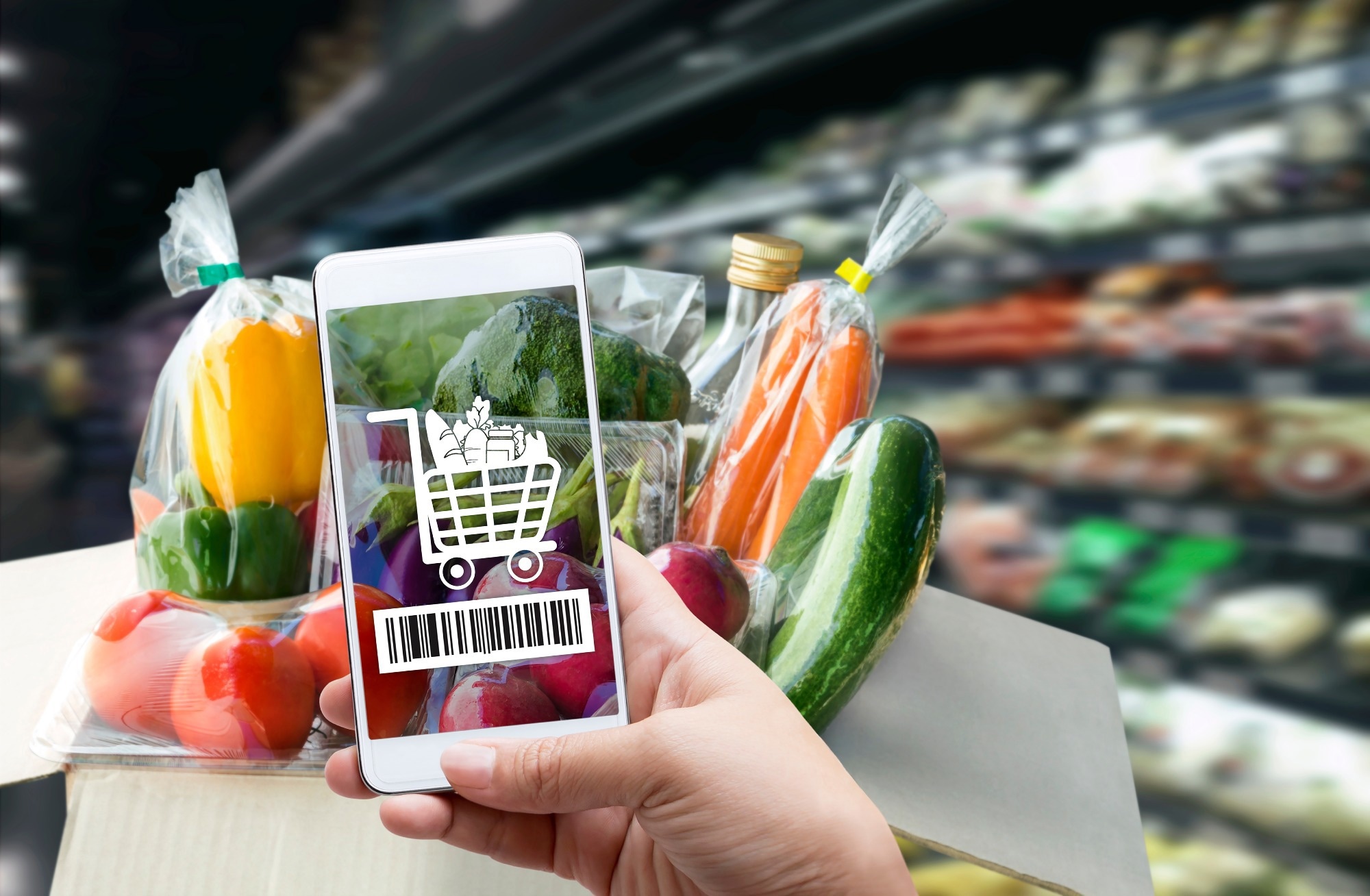
One of the most noticeable changes has taken place in the realm of personalized shopping. Using data analytics and AI algorithms, grocery retailers can now offer product suggestions tailored to individual consumer preferences, purchase history, and diet-related needs. This makes shopping more intuitive and helps customers discover relevant products they may not have otherwise considered.
In-store automation is another emerging trend driven by AI. Companies are exploring technologies such as cashier-less checkouts, robotic shelf-stocking, and smart carts equipped with vision systems. These innovations aim to reduce wait times, increase staff efficiency, and enhance the overall shopping experience, particularly in urban and high-traffic areas.
Additionally, AI has revolutionized supply chain management for grocery retailers. By anticipating demand, optimizing inventory levels, and minimizing waste, AI contributes to greater operational efficiency and sustainability. Predictive analytics can help anticipate supply disruptions and seasonal demand fluctuations, ensuring that stores remain stocked with essential goods.
Despite these promising advancements, the integration of AI into grocery shopping raises several important concerns. From an ethical standpoint, the extensive use of consumer data to power personalization algorithms may infringe on privacy rights if not handled transparently. There are concerns about how data is collected, who has access to it, and how it is used.
On a societal level, automation could lead to the displacement of traditional grocery store jobs, particularly roles like cashiers and stock clerks. The transition may create a gap in employment for low-wage workers, necessitating new labor policies and retraining programs.
Public health is another area of concern. While personalization can promote healthy choices like low-sodium or allergen-free products, it could also enable the aggressive marketing of ultra-processed foods, contributing to poor dietary habits. If not regulated, algorithms may prioritize products with higher profit margins over healthier options.
In conclusion, AI technologies are dramatically transforming grocery shopping by offering enhanced personalization, automation, and supply chain efficiency. However, they also introduce complex ethical, social, and health challenges that require proactive oversight from industry leaders, policymakers, and consumer advocates. The future of grocery retail will depend on how well these innovations are balanced with societal well-being and equitable access.
Source: https:// – Courtesy of the original publisher.